public static void watchYoutubeVideo(String id){
try{
Intent intent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW, Uri.parse("vnd.youtube:" + id));
startActivity(intent);
}catch (ActivityNotFoundException ex){
Intent intent=new Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW,
Uri.parse("http://www.youtube.com/watch?v="+id));
startActivity(intent);
}
}2016年2月8日 星期一
the youtube intent
2015年10月18日 星期日
Service-1-Start service
服務「啟動」表示應用程式元件 (例如 Activity) 透過呼叫 startService() 來啟動服務。一旦啟動,服務可以無限次數地在背景中執行,就算啟動服務的元件已終結也不會影響。 通常,已啟動的服務會執行單一操作且不會將結果傳回呼叫端。例如,服務可能會透過網路下載或上傳檔案。
服務會在其託管程序的主執行緒中執行 —
服務不會建立自己的執行緒且不會在另外的程序中執行 (除非您另行指定)。 如果您的服務即將從事任何 CPU 密集的作業或封鎖操作 (如播放 MP3 或連線網路),您應該在服務中建立新的執行緒來執行這些工作。 透過使用另外的執行緒,您會降低應用程式不回應 (ANR) 錯誤的風險,且應用程式的主執行緒仍可以專務於使用者與您的 Activity 互動。
when you call startService(intent);, will execute onCreate and onStartCommand method. However, will you call again startService, only onStartCommand will execute again.
when onStartCommand finish ,the Service object still here
當不再使用服務且正在終結服務時,系統會呼叫此方法。您的服務應該實作此方法來清除任何如執行緒、註冊的接聽器,接收器等資源。 這會是服務接收到的最後呼叫。

服務會在其託管程序的主執行緒中執行 —
服務不會建立自己的執行緒且不會在另外的程序中執行 (除非您另行指定)。 如果您的服務即將從事任何 CPU 密集的作業或封鎖操作 (如播放 MP3 或連線網路),您應該在服務中建立新的執行緒來執行這些工作。 透過使用另外的執行緒,您會降低應用程式不回應 (ANR) 錯誤的風險,且應用程式的主執行緒仍可以專務於使用者與您的 Activity 互動。
1. Create a Service
public class EchoService extends Service { public EchoService() { } @Override public void onDestroy() { super.onDestroy(); } @Override public int onStartCommand(Intent intent, int flags, int startId) { return super.onStartCommand(intent, flags, startId); } @Override public void onCreate() { super.onCreate(); } @Override public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) { // TODO: Return the communication channel to the service. throw new UnsupportedOperationException("Not yet implemented"); } }
2.At activity A start A service
Intent intent = new Intent(this,EchoService.class); startService(intent);
when you call startService(intent);, will execute onCreate and onStartCommand method. However, will you call again startService, only onStartCommand will execute again.
when onStartCommand finish ,the Service object still here
3.Stop the service
In the service :
stopSelf()
outside the Service:
stopService()
after call these method, OnDestroy() will call

2015年10月15日 星期四
Start another Activity and Get Back the Result
If:
A start B,B give back the information to A
A start B
At A activity
A start B
Reecive the information from B, onActivityResult
At B activity
B send back the information and close
A start B,B give back the information to A
A start B
At A activity
A start B
Intent intent = new Intent(this,actB.class); startActivityForResult(intent,0);
Reecive the information from B, onActivityResult
protected void onActivityResult(int requestCode, int resultCode, Intent data) { super.onActivityResult(requestCode, resultCode, data); }
At B activity
B send back the information and close
Intent i =new Intent(); i.putExtra("name","Roy"); setResult(0,i); finish();
2015年10月4日 星期日
Send Object to other Activity
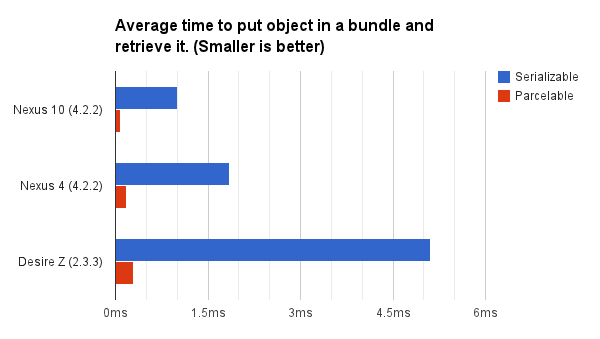
Method1(low efficiency)
use Serializable
implement Serializable the class that you want to sent
1 2 3 | class Car implements Serializable{} intent.putExtra("car",car); |
Get back the Object from intent
1 | Car c2= (Car) intent.getSerializableExtra("car"); |
Method2
use Parcelable
if i want to send a car objectFirst, implement Parcelable to car ,and override some method
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 | class Car implements Parcelable{ public Car() { } protected Car(Parcel in) { //what the code here to create the Car from a Parcel } public static final Creator<Car> CREATOR = new Creator<Car>() { @Override public Car createFromParcel(Parcel in) { return new Car(in); } @Override public Car[] newArray(int size) { return new Car[size]; } }; @Override public int describeContents() { return 0; } @Override public void writeToParcel(Parcel dest, int flags) { dest.writeString("information"); dest.writeInt(1); } } |
Put into the intent
1 | intent.putExtra("key",new Car()); |
Get back the object
1 | intent.getParcelableExtra("key"); |
Activity and Intent
Intent
use to
request an action from another app component
like
evolve, can put same information in it
Two type of Intent
Explicit intents:spefiiced to which activity
Implicit intents: don’tspefiiced to which activity,but declare a general action to perform comparing the contents of the intent to the intent filters declared in the manifest file of other apps on the device.
to find what app can be call.
Explain:
Illustration of how an
implicit intent is delivered through the system to start another activity: [1] Activity
creates an Intent with an action
description and passes it to
startActivity(). [2] The Android System searches all apps
for an intent filter that matches the intent. When a match is found, [3] the system starts the matching
activity (Activity B)
by invoking its onCreate() method and passing it
the Intent.
Android system will check all the intent filter in manifest in different app,to find the right apps,
to start another Activity by Explicit intents
if i am in Activity A, I want to start the Activity B
1 2 3 | Intent intent = new Intent(this,B.class); intent.putExtra("name","vlue");// put other information on to the intent startActivity(intent); |
Send informatiom to other Activity
At Activity B, I want to get back the information that i put into the intent
1 2 | Intent intent = getIntent(); String s=intent.getStringExtra("name"); |
Bundle
bundle is like a box, we can put many thing in it.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 | put bundle into the intent Bundle bundle=new Bundle(); bundle.putChar("key", 'v'); intent.putExtra("bundle", bundle); get value form the bundle Bundle bundle1=intent.getBundleExtra("bundle"); bundle1.getChar("key"); |
Some common intent use in
explain Component
name, Action, Data, Category
http://developer.android.com/guide/components/intents-filters.html
Intent and the Filter
ref:http://jasonandroid.blogspot.hk/2013/10/intents-and-intent-filters.html
Explicit intents vs Implicit intents and intent filter
A intent can hold Component name, Action, Data, Category,Extra and Flag
if not have Component name,the intent is a Implicit intents
Component name
Action
A string that specifies the generic action to perform (such as view or pick).
the defined action
Data
Category
kind of component that should handle the intent.
Extra
Flag
how to create a intent filter for a Activity?
we need to think abou whta action that the activity what to do,than set the app right data ,action and ategory
a intentFilter at last have on action
if a activity want to receive Implicit intents,must have
<category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT"/>
example
How to compare the Intent and the rule of compare the Data?
https://developer.android.com/guide/components/intents-filters.html
action test,data test(type and data),Category test
Action test
in the filter,can have one or more action
How to pass?
if the intent want to pass the test,one action match is ok
if intent filter have no action,no intent can pass the test
if intent has no action,but the filter have one or more action,the intent pass the test
Data test(type and data)
data can
<scheme>://<host>:<port>/<path>
For example:
content://com.example.project:200/folder/subfolder/etc
example
<intent-filter>
<data android:mimeType="video/mpeg" android:scheme="http" ... />
<data android:mimeType="audio/mpeg" android:scheme="http" ... />
...
</intent-filter>
<intent-filter>
<data android:mimeType="image/*" />
...
</intent-filter>
important:
Each of these attributes is optional in a <data> element, but there are linear dependencies:
If a scheme is not specified, the host is ignored.
If a host is not specified, the port is ignored.
If both the scheme and host are not specified, the path is ignored.
Compare the dtat
compared only to the parts of the URI included in the filter. For example:
If a filter specifies only a scheme, all URIs with that scheme match the filter.
If a filter specifies a scheme and an authority but no path, all URIs with the same scheme and authority pass the filter, regardless of their paths.
If a filter specifies a scheme, an authority, and a path, only URIs with the same scheme, authority, and path pass the filter.
The data test compares both the URI and the MIME type in the intent to a URI and MIME type specified in the filter. The rules are as follows:
- An intent that contains neither a URI nor a MIME type passes the test only if the filter does not specify any URIs or MIME types.
- An intent that contains a URI but no MIME type (neither explicit nor inferable from the URI) passes the test only if its URI matches the filter's URI format and the filter likewise does not specify a MIME type.
- An intent that contains a MIME type but not a URI passes the test only if the filter lists the same MIME type and does not specify a URI format.
- An intent that contains both a URI and a MIME type (either explicit or inferable from the URI) passes the MIME type part of the test only if that type matches a type listed in the filter. It passes the URI part of the test either if its URI matches a URI in the filter or if it has a
content: or file: URI and the filter does not specify a URI. In other words, a component is presumed to support content: and file: data if its filter lists only a MIME type.
Category test
Filter can have 0 or more categorycontent: or file: URI and the filter does not specify a URI. In other words, a component is presumed to support content: and file: data if its filter lists only a MIME type.How to pass?
all the Category in the intent must match the Category in the filter,
the other Category in the filter no need to consider
intent have no Category ,must pass the test
important!!!!
if intent send by startActivity()
CATEGORY_DEFAUL will add,so the filter must have CATEGORY_DEFAULT
if filter already have CATEGORY.LAUNCGER and CATEGORY.DEFAULT,no need CATEGORY_DEFAULT
訂閱:
文章 (Atom)
